
The Stroke Network
PO Box 492
Abingdon, MD 21009
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
Some oral antidepressants and anticonvulsants can be useful in treating
mild central pain syndrome. Older antidepressant drugs such
as amitriptyline (Elavil) appear to reduce the pain, but they have side
effects of sleepiness, dry mouth, and dizziness. A newer
antidepressant drug called duloxetine (Cymbalta) is also used for
central pain syndrome; this drug has less of these undesirable side
effects than amitriptyline.
Antiepileptic
drugs (AEDs) appear to affect the transmission of the sensory nerves
that result in central pain. The most commonly used AEDs for central
pain syndrome are gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin
(Lyrica). Other AEDs sometimes used in treatment of pain
include carbamazepine (Tegretol) and topiramate (Topamax).
With time,
pain may increase in intensity. As pain eventually becomes
worse, treatment may progress through increasingly strong analgesics
and possibly up to narcotics.
Narcotics
are the best drugs for pain because they bind specifically to pain
receptors. Narcotic analgesics like morphine, methadone and
heroin are very effective.
In cases
where spasticity and stiffness are a contributor to pain, oral Baclofen
may be prescribed. High dosages of oral Baclofen may cause
serious
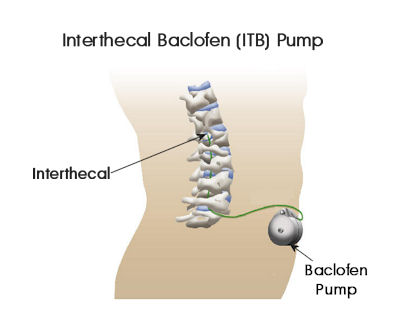
side-effects. An implanted Interthecal
Baclofen (ITB) Pump, which has virtually no side-effects, may
become necessary.
With an
implanted pump, small amounts of the drug are delivered from the pump
flowing to the fluid around the spinal cord. Thus, only tiny
amounts of drugs are affecting the central nervous system.
|
|
 |
Stroke
Warning Signs
 |
Sudden numbness or weakness of the face, arm
or leg, especially on one side of the
body |
 |
Sudden confusion, trouble speaking or
understanding |
 |
Sudden trouble seeing in one or both
eyes |
 |
Sudden trouble walking, dizziness, loss of
balance or coordination |
 |
Sudden, severe headache with no known cause |

|

